CCAT Practice Test Questions and test information
- Posted by Brian Stocker
- Date November 4, 2020
- Comments 4 comments
About the test
The Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test is a cognitive test often used for admissions to gifted programs throughout Canada. It is aimed at evaluating the cognitive abilities of students in K-12 grades. The test is the Canadian version of the CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test), which is given in the United States.
Assesses academic strengths and weaknesses in children to be admitted into Canadian gifted and talented programs n grade 1. The test assesses verbal, nonverbal, and quantitative abilities. The test focuses less on verbal abilities than nonverbal and quantitative skills, and is very useful for students who do not speak English natively.
Test Format
The CCAT is a lengthy test, and the three batteries are often given in separate testing sessions, sometimes even on different days. Administration time may vary, depending on how long the proctor takes to administer the test. Students are generally given between 30–45 minutes to complete each battery. It takes between two and three hours to complete all three batteries. In total, the CCAT has between 118 and 176 questions, depending on the level.
Start with a CCAT Practice Test
Scoring
Scores received are a composite of all three of the CCAT batteries with three different scores. The Age Percentile Rank (APR) ranks a student with others in his or her age group, whereas the Grade Percentile Rank (GPR) ranks a student within their grade. The final score, the Stanine (S) score, relays a specific range of scores that have predetermined ranks-—9 being very high, 1 being very low, and 4–6 being average.
You get your report immediately after you complete the test. The results and interpretations of the test can be explained using four categories:
- Raw Score
Once you take the CCAT Test, you will be provided with a raw score. A raw score indicates the number of questions answered correctly. For instance, if your raw score is 30, it means that you have correctly answered 30 out of 50 questions.
The average raw score is 24.
- Percentile Ranking
The raw score is converted into a relative performance metric called ‘percentile ranking.’ This indicates your score in comparison to others who have taken the test. For instance, if your percentile ranking is 44, it means that you scored better than 44% of test-takers.
- Sub-Scores
You also receive separate scores for each of the three sections: (1) logic and math, (2) verbal ability, and (3) spatial reasoning. The scores you receive in these categories are percentiles, meaning that if you scored a 25 in logic and math, 50 in verbal ability, and 75 in spatial reasoning:
25 = you scored better than 25% of other test-takers in logic and math
50 = you scored better than 50% of other test-takers in verbal ability
75 = you scored better than 75% of other test-takers in spatial reasoning
CCAT Test Content – All Levels
The Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test has 7 levels, one for each grade starting at kindergarten:
CCAT Kindergarten (Level 5/6), CCAT Grade 1 (Level 7), CCAT Grade 2 (Level 8), CCAT Grade 3 (Level 9), CCAT Grade 4 (Level 10), CCAT Grade 5 (Level 11) and CCAT Grade 6 (Level 12)
The test has three sections called batteries: The Verbal Battery, the Nonverbal Battery, and the Quantitative Battery. These batteries can be administered separately or together, depending on the school’s specific needs or the teacher administering the test.
The Verbal Battery tracks how students apply language to reasoning. Students are tested based on their comprehension of language structure and word relationships. Questions include verbal classification, sentence completion, and verbal analogies.
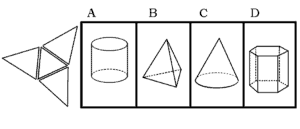
The Nonverbal Battery evaluates spatial abilities independent of language. Questions include many diagrams and visual aids. Students are asked to apply their knowledge to figure classifications, figure analogies, and figure analysis. The Nonverbal Battery measures explicitly reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
The Quantitative Battery assesses number skills. Reasoning and problem-solving skills are tracked based on mathematical ability and numerical application. Questions include quantitative relations, number series, and equation building.
CCAT practice test questions for each level below.
Verbal Battery
The verbal battery contains
- Picture analogies
- Sentence completion
- Picture classification
The verbal reasoning section tests reasoning and comprehension, and the use language for reasoning tasks.
Why Verbal Reasoning is important
- Conceptual Thinking: Verbal tasks, especially those involving classification, require your child to identify relationships between different words or concepts
- Language Proficiency: tests a child’s ability to understand, use and assimilate language. This is a critical skill and predictor of academic success, as well as daily communication and various types of interactions.
- Predictor of Academic Success: Proficiency in the verbal section is an excellent predictor of a child’s future achievements in social studies, language arts, , and related disciplines.
- Identifying Needs: The verbal section can guide teachers in instruction and intervention strategies to improve children’s language and reasoning ability.
Verbal Battery Practice
Sentence Completion (meaning in context)
Picture Analogies (IQ type)
Quantitative Battery
The Quantitative Battery assess a student’s ability to understand and analyze numerical concepts and relationships, use logical reasoning, apply mathematical concepts and solve mathematical problems, and reason using numbers. All of these cognitive skills are essential for problem-solving in many different contexts.
The quantitative battery contains:
- Number analogies
- Number series
- Number puzzles
Why the Quantitative Battery is Important
Evaluates Numerical Proficiency: The quantitate battery assesses the ability to understand, work with, and infer information based on numerical data. This is a critical skill in many mathematical applications in academic and daily life.
Predicting Academic Success: This section identifies students who might need additional tutoring support in mathematical areas and predicts future success.
Quantitative Battery Practice
Nonverbal Battery
The Nonverbal Battery presents the test taker with geometric shapes and figures, and asks them to identify relationships between pictures in a matrix, determine how a shape will look when folded or unfolded, and recognizing patterns in a set of shapes and choosing the next figure in the sequence.
The nonverbal battery contains:
- Figure matrices
- Figure classification
- Paper folding
Non Verbal Battery Practice
CCAT Practice Test Questions and Study Packs
Date Published: Wednesday, November 4th, 2020
Date Modified: Monday, April 15th, 2024
Got a Question? Email me anytime - Brian@test-preparation.ca
You may also like
Hard Algebra Questions
Advanced Algebra Practice 1. Simplify expressions with radicals and rational exponents using properties of exponents A = 22a – 2 and B = 53 – 2a are given. Find the value of 404a – 2 in terms of A and …
Comprensión Lectora de Opción Múltiple
Aumenta tu Puntuación Passage 1 – El uso de las redes sociales en la adolescencia se relaciona con la pobreza Sueño, ansiedad. Fuente: [Por Agata Blaszczak-Boxe, publicado originalmente en Live Science, septiembre de 2015]. Según un nuevo estudio, la presión …
Spatial Relations – Blocks and Touching Blocks
Touching Blocks Touching Blocks questions give a complex image of blocks and you are asked to count the number of blocks a given block is touching. Blocks – Cubes Blocks questions present a complex geometric figure made of a series …

4 Comments
I really like to learn and thank you for making this site
oh i also like to learn milana
Very helpful thanks!
very comprehensive thanks!!