
How to Solve Quadratic Equations – Tutorial, Examples and Practice Questions
- Posted by Brian Stocker MA
- Date April 6, 2014
- Comments 2 comments
Polynomials
In algebra, a quadratic equation is any equation having the form where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c represent known numbers such that a is not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic.
Quadratic equations are usually called second degree equations, which mean that the second degree is the highest degree of the variable that can be found in the quadratic equation.
Solving Quadratic equations appear on most standardized tests and some High School Proficiency exams
How to Solve Quadratic Equations
Method 1 – Factoring
Quadratic equations are usually called second degree equations, which mean that the second degree is the highest degree of the variable that can be found in the quadratic equation. The form of these equations is:
where a, b and c are some real numbers.
One way for solving quadratic equations is the factoring method, where we transform the quadratic equation into a product of 2 or more polynomials. Let’s see how that works in one simple example:
Notice that here we don’t have parameter c, but this is still a quadratic equation, because we have the second degree of variable x. Our factor here is x, which we put in front and we are left with x+2. The equation is equal to 0, so either x or x+2 are 0, or both are 0.
So, our 2 solutions are 0 and -2.
Method 2 – Quadratic formula
If we are unsure how to rewrite quadratic equations so we can solve it using factoring method, we can use the formula for quadratic equation:
We write x1,2 because it represents 2 solutions of the equation. Here is a practice question :
We see that a is 3, b is -10 and c is 3.
We use these numbers in the equation and do some calculations.
Notice that we have + and -, so x1 is for + and x2 is for -, and that’s how we get 2 solutions.

Solving Quadratic Practice Questions
1. Find 2 numbers that sum to 21 and the sum of the squares is 261.
a. 14 and 7
b. 15 and 6
c. 16 and 5
d. 17 and 4
2. Using the factoring method, solve the quadratic
equation: x2 + 4x + 4 = 0
a. 0 and 1
b. 1 and 2
c. 2
d. -2
3. Using the quadratic formula, solve the quadratic
equation: x – 31/x = 0
a. -√13 and √13
b. -√31 and √31
c. -√31 and 2√31
d. -√3 and √3
4. Using the factoring method, solve the quadratic
equation: 2x2 – 3x = 0
a. 0 and 1.5
b. 1.5 and 2
c. 2 and 2.5
d. 0 and 2
5. Using the quadratic formula, solve the quadratic
equation: x2 – 9x + 14 = 0
a. 2 and 7
b. -2 and 7
c. -7 and -2
d. -7 and 2
Answer Key
1. B
There are two statements made, which can be written as two equations:
The sum of two numbers are 21: x + y = 21
The sum of the squares is 261: x2 + y2 = 261
We are asked to find x and y.
Since we have the sums of the numbers and the sums of their squares; we can use the square formula of x + y, that
is:
(x + y)2 = x2 + 2xy + y2 … Here, we can insert the known values x + y and x2 + y2:
(21)2 = 261 + 2xy … Arranging to find xy:
441 = 261 + 2xy
441 – 261 = 2xy
180 = 2xy
xy = 180/2
xy = 90
We need to find two numbers which multiply to 90. Checking the answer choices, we see that in (b), 15 and 6 are
given, which sum to 90 (15 * 6 = 90) and their squares sum to 261 (152 + 62 = 225 + 36 = 261).
2. D
x22 + 4x + 4 = 0 … We try to separate the middle term 4x to
find common factors with x22 and 4 separately:
x22 + 2x + 2x + 4 = 0 … Here, we see that x is a common
factor for x22 and 2x, and 2 is a common factor for 2x and 4:
x(x + 2) + 2(x + 2) = 0 … Here, we have x times x + 2 and
2 times x + 2 summed up. This means that we have x + 2
times x + 2:
(x + 2)(x + 2) = 0
(x + 2)2 = 0 … This is true if only if x + 2 is equal to zero.
x + 2 = 0
x = -2
3. B
To solve the equation, first we need to arrange it to appear in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0 by removing the denominator:
x – 31/x = 0 … First, we enlarge the equation by x:
x * x -31 * x/x = 0
x2 – 31 = 0
The quadratic formula to find the roots of a quadratic equation is:
x1,2 = (-b ± √∆) / 2a where ∆ = b2 – 4ac and is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
In our question, the equation is x2 – 31 = 0. By remembering the form ax2 + bx + c = 0:
a = 1, b = 0, c = -31
So, we can find the discriminant first, and then the roots of the equation:
∆ = b2 – 4ac = 02 – 4 * 1 * (-31) = 124
x1,2 = (-b ± √∆) / 2a = (±√124) / 2 = (±√4 * 31) / 2
= (±2√31) / 2 … Simplifying by 2:
x1,2 = ±√31 … This means that the roots are √31 and -√31.
4. A
2x2 – 3x = 0 … we see that both of the terms contain x; so we can take it out as a factor:
x(2x – 3) = 0 … two terms are multiplied and the result is zero. This means that either of the terms or both of the
terms can be equal to zero:
x = 0 … this is one solution
2x – 3 = 0
2x = 3
x = 3/2
x = 1.5 … this is the second solution.
So, the solutions are 0 and 1.5.
5. A
To solve the equation, we need the equation in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0.
x2 – 9x + 14 = 0 is already in this form.
The quadratic formula to find the roots of a quadratic equation is:
x1,2 = (-b ± √Δ) / 2a where Δ = b2 – 4ac and is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
In our question, the equation is x2 – 9x + 14 = 0. By remembering the form ax2 + bx + c = 0:
a = 1, b = -9, c = 14
So, we can find the discriminant first, and then the roots of the equation:
Δ = b2 – 4ac = (-9)2 – 4 * 1 * 14 = 81 – 56 = 25
x1,2 = (-b ± √Δ) / 2a = (-(-9) ± √25) / 2 = (9 ± 5) / 2
This means that the roots are,
x1 = (9 – 5) / 2 = 2 and x2 = (9 + 5) / 2 = 7
Date Published: Sunday, April 6th, 2014
Date Modified: Thursday, July 13th, 2023
You may also like

Basic Math Video Tutorials

How to Answer Basic Math Multiple Choice

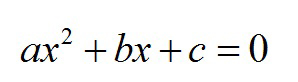
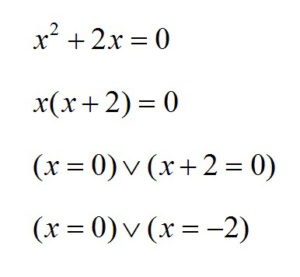
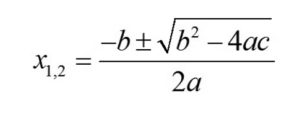
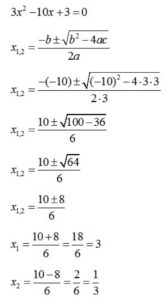
2 Comments
Very helpful
A Very good way to learn